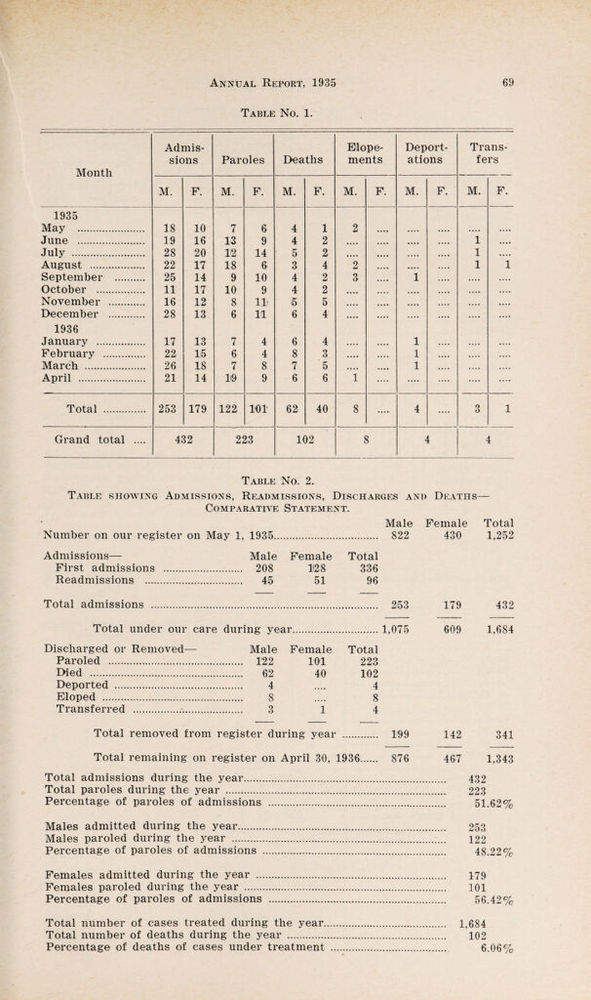
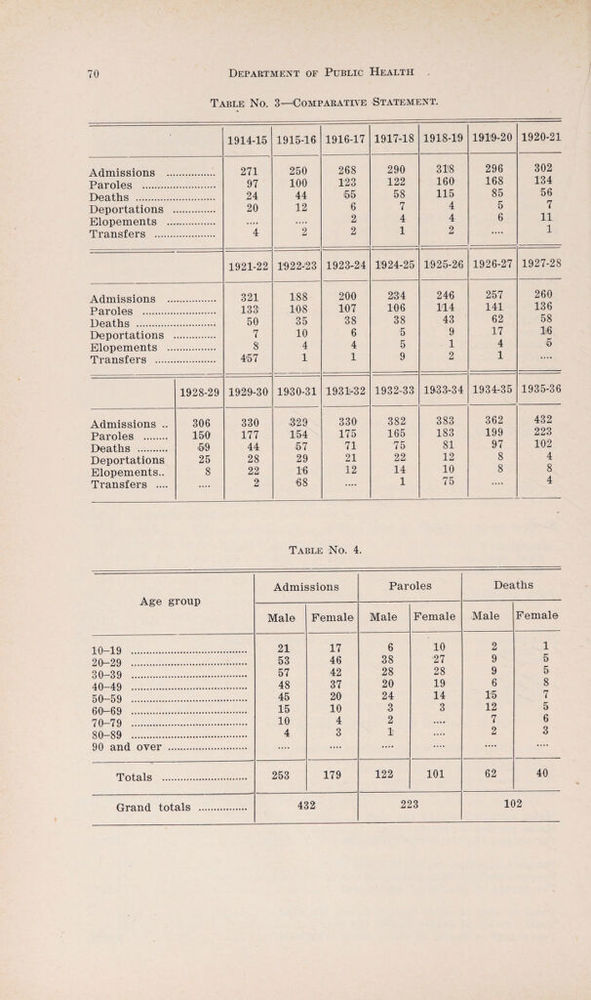
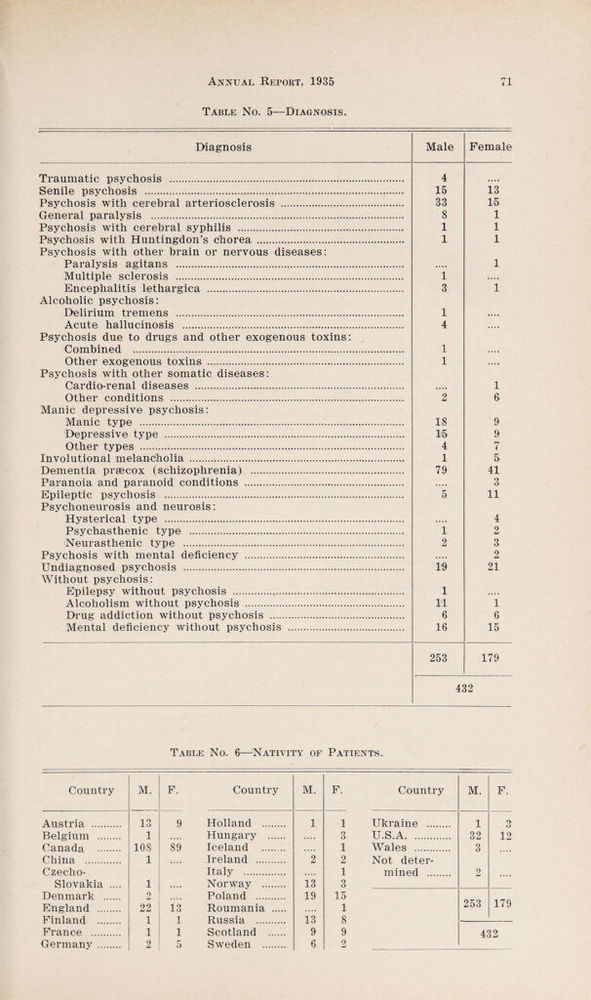
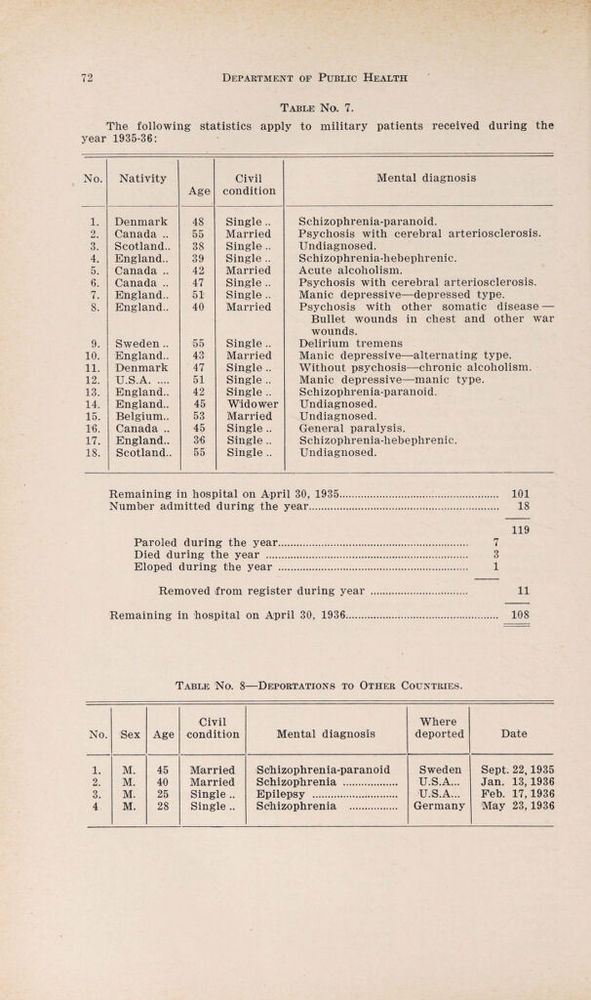
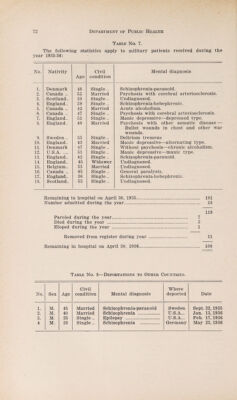
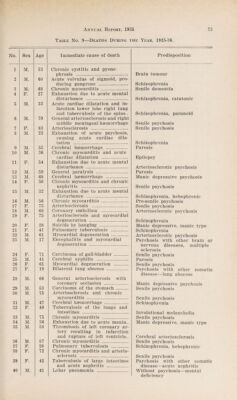
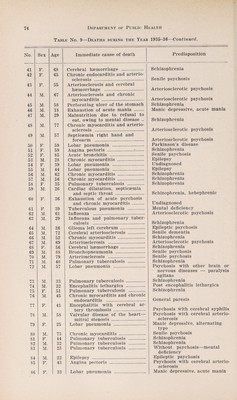
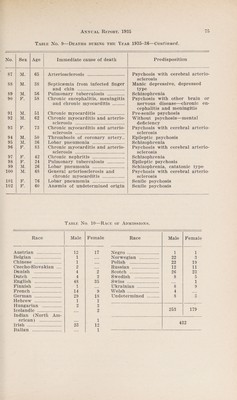
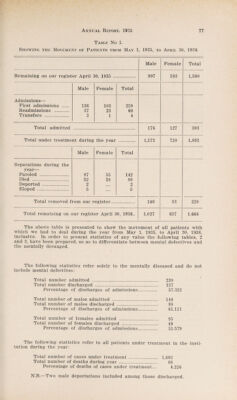
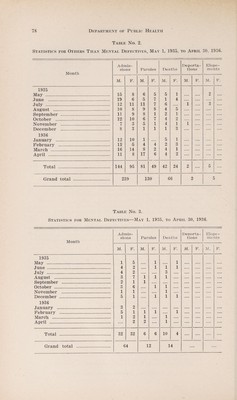
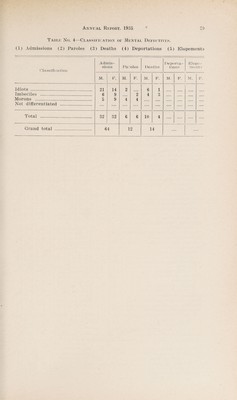
Annual report of the Department of Public Health of the Province of Saskatchewan.
- Saskatchewan. Department of Public Health.
- Date:
- [1935]
Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: Annual report of the Department of Public Health of the Province of Saskatchewan. Source: Wellcome Collection.