Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: Heart-beat and pulse-wave / by C.S. Roy and J.G. Adami. Source: Wellcome Collection.
Provider: This material has been provided by the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh. The original may be consulted at the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh.
63/88 (page 415)
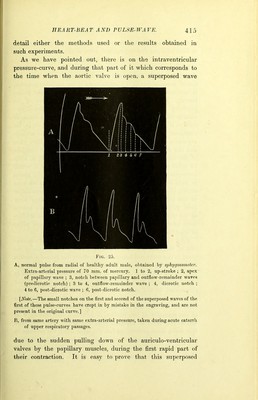
![detail either the methods used or the results obtained in such experiments. As we have pointed out, there is on the intraventricular pressure-curve, and during that part of it which corresponds to the time when the aortic valve is open, a superposed wave Fig. 25. A, normal pulse from radial of healthy adult male, obtained by sphygmometer. Extra-arterial pressure of 70 mm. of mercury. 1 to 2, up-stroke ; 2, apex of papillary wave ; 3, notch between papillary and outflow-remainder waves (predicrotie notch) ; 3 to 4, outflow-remainder wave ; 4, dicrotic notch ; 4 to 6, post-dicrotic wave ; 6, post-dicrotic notch. [Note.—The small notches on the first and second of the superposed waves of the first of these pulse-curves have crept in by mistake in the engraving, and are not present in the original curve.] 15, from same artery with same extra-arterial pressure, taken during acute catarrh of upper respiratory passages. due to the sudden pulling down of the auriculo-ventricular valves by the papillary muscles, during the first rapid part of their contraction. It is easy to prove that this superposed](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b21908515_0065.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)