Licence: In copyright
Credit: General and practical optics / by Lionel Laurance. Source: Wellcome Collection.
Provider: This material has been provided by UCL Library Services. The original may be consulted at UCL (University College London)
296/390 page 286
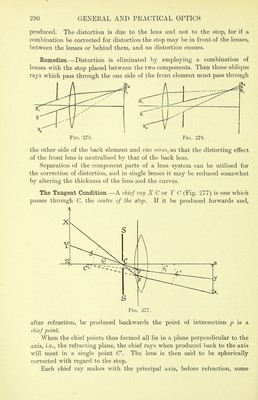
![h in Pi, but T T\ as already stated, lies nearer the lens than B R', and both are nearer than F. Radial astigmatism has been illustrated with the light diverging from a point on the lower edge of an object, so that the resulting tangential focal line is horizontal and the radial line is vertical. If the luminous point is to the right or left of the object, the tangential line is vertical and the radial line horizontal; if the sagittal plane is oblique both lines are oblique, there being a pair of astigmatic lines at right angles for each secondary axis. The tangential and radial lines of the numberless secondary axes consti- FiG. 270. tute curved surfaces (Fig. 271), both within the principal focal plane; these curved surfaces meet at the principal axis in the focal plane, where the two focal lines fuse into a point image. The circles of least confusion form a surface 0 0' concave towards the lens lying between R R' and T V and this may be regarded as the focal plane of an ordinary lens. Influencing Factors.—Radial astigmatism is in direct proportion to the obliquity of the incident light, and is greater as the lens aperture is larger. Fig. 271. It is also greater with certain forms of lenses than others, and, in general, the more nearly a lens is of double Cx. form the more marked it is. Remedies.—Anything that tends to equalise the effective thickness of the lens and the angles of incidence in all meridians will reduce radial astig- matism. Thus a meniscus lens combined with a stop to cut off the extreme peripheral rays is the primary remedy, especially if the stop be placed some little distance—about a fifth the focal length—on the concave side. This has the effect of shortening both focal lines and throwing them back so that the circle of least confusion lies more nearly in the foca] plane; by still](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b21287946_0296.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)