Report of the Director-General of Public Health, New South Wales.
- New South Wales. Department of Public Health
- Date:
- [1932]
Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: Report of the Director-General of Public Health, New South Wales. Source: Wellcome Collection.
29/174 page 11
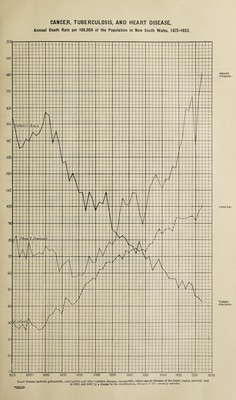
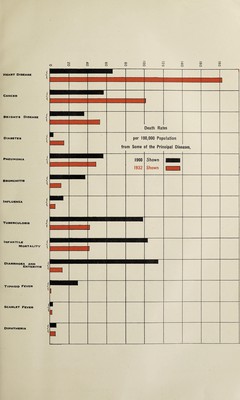
![respectively; and in 1932 the deaths of males numbered 582 and of females 387, and the rates per million living were 453 and 310. The mortality from other tuberculous diseases was 25 per cent, below the average in 1931 and 23 bolow in 1932. Cancer.—In 1931 the deaths from cancer numbered 2,439, equal to a rate of 972 per million living, and 4 per cent, above the average of the preceding quinquennial period. The deaths of males numbered 1,256 and of females 1,173, the rates for each sex being 993 and 949 per million respectively. In 1932 the deaths from cancer numbered 2,534. equal to a rate of 1,001 per million living, and 6 per cent, above the average of the preceding quinquennial period. The deaths of males numbered 1,405 and of females 1,129, the rates for each sex being 1,094 and 905 per million respectively. The death-rate from this disease has been increasing steadily for a number of years. Diseases of the Heart were the cause of 4,188 deaths in 1931, the rate being 1,668 per million. In 1932 there were 4,587 deaths, the rate being 1,812 per million. The apparent increase in these deaths during the last twenty-five years is probably the result of more careful death certifications. Furthermore, in combination with other diseases, where precise information is lacking, diseases of the heart are given precedence over many other diseases. Deaths from heart diseases in 1931 were 9 per cent, and in 1932 15 per cent, above the average of the preceding five years. Of the total deaths in 1931, 2,359 were of males and 1,829 of females, the corresponding rates per million living of each sex being 1,851 and 1,480; in 1932 of the total deaths 2,630 were of males and 1,957 females, the corresponding rates of each sex being 2,048 and 1,569 per million respectively. Bronchitis and Pneumonia.—In 1931 bronchitis with 366 deaths (equal to a rate of 146 per million living) showed a decrease of 18 per cent.; and pneumonia with 1,398 deaths, or 557 per million, a decrease of 23 per cent, as compared with the experience of the previous five years. In 1932 there were 302 deaths from bronchitis, equal to a rate of 119 per million living, or a decrease of 30 per cent.; and pneumonia with 1,239 deaths, or 489 per million, a decrease of 30 per cent, as compared with the experience of the previous five years. Of the deaths from bronchitis in 1931, 176 were of males and 190 of females, or 138 and 154 per 1,000,000 living respectively; and in 1932, 173 were of males and 129 of females, or 135 and 103 per million living respectively. Of the persons who died from pneumonia in 1931, 818 were males and 580 were females, and the rates were 642 and 469 per million living of each sex. In 1932, 720 males and 519 females died from pneumonia, the rates being 561 and 416 per million living of each sex. Bright’s Disease.—During 1931 there were 1,678 deaths due to diseases of the genitourinary system, of which 1,311 were caused by acute nephritis and Bright’s disease. The rate for nephritis (acute and chronic) was 522 per million; for males 575 and for females 468 per million. In 1932 there were 1,780 deaths due to diseases of the genitourinary system, of which 1,371 were caused by acute nephritis and Bright’s disease. The rate for nephritis (acute and chronic) was 542 per million; males 610, and females 471 per million. Diseases of Infants.—In both 1931 and 1932 the principal causes were prematurity, 682 and 629 respectively; other developmental diseases, 586 and 608; diarrhoea and enteritis, 212 and 126, pneumonia, 198 and 172; whooping cough, 114 and 44; bronchitis, 31 and 22; measles, 7 and 2, and convulsions, 10 and 13. The following statement shows the causes of deaths of children under 1 year of age per 1,000 births during 1931 and 1932, in comparison with the preceding five years:— 1931. Causes of Death. Males. Females. Tol al. 103 J. 1926-30. 1931. 1926-30. 1931. 1026-30. Epidemic Diseases . 3-42 3-58 3-88 3-65 3-65 3-62 Tuberculous Diseases . •20 •28 •30 •35 •25 •32 Syphilis . •33 •29 •22 •29 •27 •29 Menino'iti.s . •16 •68 •17 •51 ■17 •60 Convulsions . •16 •74 •26 •52 •21 •63 Bronchitis . •61 •97 •69 •83 •65 •CO Pneumonia . 4-77 6-04 3-49 5-19 4-15 5-62 Diarrhoea and Enteritis . 5-21 9-91 3-62 8-05 4-44 8-01 Prcmatuio Birth . 15-85 17-82 12-64 14-25 14-29 16-09 Other Developmental Diseases . 14-42 15-96 1001 12-05 12-28 14-03 Other Causes . 3-59 4-12 2-72 3-16 316 3-Co All Causes . 48-73 6041 384)1 48-83 43-52 54-78 1932. Causes of Death. Males. Female: 1 Total. 1932. 1927-31. 1932. j 1927-31. 1 1932. j 19 27-31. Kp id Dm if*. nipniLPnR . 2-08 3-58 ICO 3*05 1-S9 3-71 .90 •28 •23 •15 •22 •30 Kvnhilis ... .oc> •32 •29 •27 •29 Mem ip cntdfl . ••• •C6 •08 / O , •51 •45 •51 •17 •74 •41 .r;o i LUJ •29 •47 •GO •97 •37 •83 •49 •86 4-50 6-04 3-12 519 3-83 2-80 1 5*57 2-85 9-91 2-75 8-05 7-61 ]>rf'mpJtnrn RirtH . 15-70 17-82 12-21 14-25 14-01 | 15-60 15-10 15-86 11-89 12-05 13-54 13-73 Othe r Causes. 3-55 412 2-98 i 316 3-27 350 All Causes . 45-53 00-41 36-30 48-83 4 TOG 52-15 1](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b31485236_0029.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)