The solubilities of the pharmacopœial organic acids and their salts / by Atherton Seidell.
- Seidell, Atherton, 1878-1961.
- Date:
- [1910]
Licence: In copyright
Credit: The solubilities of the pharmacopœial organic acids and their salts / by Atherton Seidell. Source: Wellcome Collection.
62/104 (page 60)
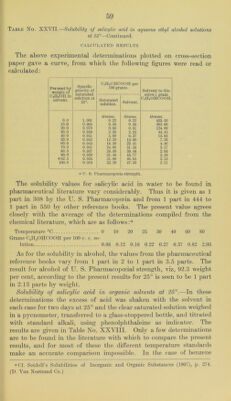
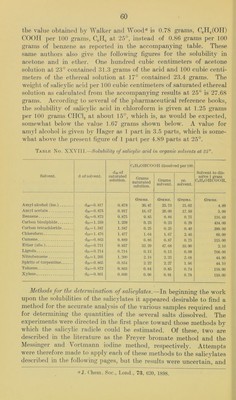
![the value obtained by Walker and Wood® is 0.78 grams, CgH^COH) coon per 100 grams, CJIo at 25°, instead of 0.86 grams per 100 grams of benzene as reported in the accompanying table. These same authors also give the following figures for the solubility in acetone and in ether. One hundred cubic centimeters of acetone solution at 23° contained 31.3 grams of the acid and 100 cubic centi- meters of the ethereal solution at 17° contained 23.4 grams. The weight of salicylic acid per 100 cubic centimeters of saturated ethereal solution as calculated from the accompanying results at 25° is 27.68 grams. According to several of tlie pharmaceutical reference books, the solubility of salicylic acid in chloroform is given at 1.25 grams per 100 grams CHCI3 at about 15°, which is, as would be expected, somewhat below the value 1.67 gi'ams shown below. A value for amyl alcohol is given by TIager as 1 ])art in 3.5 parts, which is some- what above the present figure of 1 part per 4.89 parts at 25°. Table No. XXVIII.—Solubility of salicylic acid in organic solvents at 25°. d26 of saturated solution. C(jinOHCOOH dissolved per 100. Solvent to dis- solve 1 gram CoinOIICOOH. Solvent. d of solvent. Grams saturated solution. Grams solvent. cc. solvent. Amyl alcohol (iso.) d2o=0.817 0.878 Grams. 20.47 Grams. 25.73 Grams. 21.02 Grams. 4.89 Amyl acetate d2o=0* 875 0.917 10.07 20.00 17.50 5.00 Benzene d2i=0.873 0.875 0.85 0.86 0.75 116. (iO Carbon bisulphide d25= 1.259 1.259 0.23 0.23 0.29 434.00 Carbon tetrachloride d2o= 1.587 1.587 0.25 0.25 0.40 399.00 Chloroform d23= 1.476 1.477 1.04 1.67 2.46 60.00 Cumene d2o=0.863 0.889 0.86 0.87 0. 75 115.00 Ether (abs.) d22= 0.711 0.857 32.29 47.68 33.90 2.10 Ligroin d23=0. 714 0.714 0.13 0.13 0.09 768.00 Nitrobenzene d23= 1.205 1.200 2.18 2. 23 2.68 44.90 Spirits of turpentine d2o=0.865 ■0. 854 2. 22 2.27 1.96 44.10 Toluene di5= 0.872 0.863 0.84 0.85 0. 74 118.00 Xylene ^4 00 0 11 0.860 0.90 0.91 0.78 110.00 Methods for the determination of salicylates.—In beginning the work upon the solubilities of the salicylates it appeared desirable to find a method for the accurate analysis of the various samples required and for determining the quantities of the several salts dissolved. The experiments were directed in the first place toward those methods by which the salicylic radicle could be estimated. Of these, two are described in the literature as the Freyer bromate method and the Messinger and Vortmann iodine method, respectively. Attempts were therefore made to apply each of these methods to the salicylates described in the following pages, but the results were uncertain, and aj. ('hem. Soc., Lend., 73, G20, 1898.](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b28063909_0062.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)