The final interim report by the work group for studying the effects of the specific health checkups and specific health guidance on health care expenditures / The Work Group for Studying the Effects of the Specific Health Checkups and Specific Health Guidance on Health Care Expenditures ; Fukuda Takashi (work group member) [and 5 others] ; Hosurā Akiko (consultant).
- Japan. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW)
- Date:
- [2015]
Licence: Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Credit: The final interim report by the work group for studying the effects of the specific health checkups and specific health guidance on health care expenditures / The Work Group for Studying the Effects of the Specific Health Checkups and Specific Health Guidance on Health Care Expenditures ; Fukuda Takashi (work group member) [and 5 others] ; Hosurā Akiko (consultant). Source: Wellcome Collection.
20/260 (page 12)
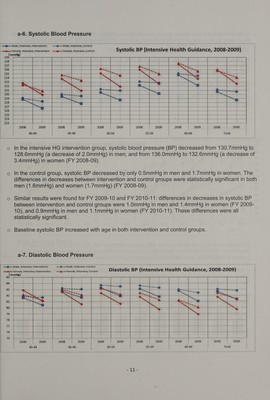
![81.4mmHg (a decrease of 1.3mmHg) in men, and from 81.8mmHg to 79.7mmHg (a decrease of 2.0mmHg) in women (FY 2008-09). ' In the control group, diastolic BP decreased by only 0.2mmHg in men and 1.0mmHg in women. The differences in decreases between intervention and control groups were statistically significant in both men (1.0mmHg) and women (1.0mmHg) (FY 2008-09). Similar results were found for FY 2009-10 and FY 2010-11: the differences in decreases in diastolic BP between intervention and control groups were 0.7mmHg in both men and women (FY 2009-10), and 0.6mmbg in both men and women (FY 2010-11). These differences were all statistically significant. a-8. Triglycerides | mii Viale, Intensive, Intervention = <@ — Male, Intensive, Control | —-—— Female, Intensive, Intervention te = Female, intensive, Control wie eb Triglyceride (Intensive Health Guidance, 2008-2009) 200 | 190 | 120 110 -| a Moe ] = | e Mh | e ~ +. 2009 50-54 | 2009 =| 2008 2008 | 2009 2008 += —=—.2009 45-49 | | 2008 | 2009 2008 | 2008 2009 40-44 55-59 60-64 Total In the intensive HG intervention group, triglycerides dropped from 191.7mg/dl to 164.5mg/dl (a decrease of 27.2mg/dl) in men, and from 165.7mg/dl to 139.3mg/dl (a decrease of 26.4mg/dl) in women (FY 2008-09). In the control group, triglycerides decreased by only 10.4mg/dl in men and 12.1mg/dl in women. The differences in decreases between intervention and control groups were statistically significant in both men (16.8mg/dl) and women (14.3mg/dl) (FY 2008-09). Similar results were found for FY 2009-10 and FY 2010-11: the differences in deceases of triglycerides between intervention and control groups were 11.5mg/dl in men and 9.9mg/dl in women (FY 2009-10), and 7.7mg/dl in men and 8.3mg/dl in women (FY 2010-11). These differences were all statistically significant. 3 rin](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b32222762_0020.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)