The final interim report by the work group for studying the effects of the specific health checkups and specific health guidance on health care expenditures / The Work Group for Studying the Effects of the Specific Health Checkups and Specific Health Guidance on Health Care Expenditures ; Fukuda Takashi (work group member) [and 5 others] ; Hosurā Akiko (consultant).
- Japan. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW)
- Date:
- [2015]
Licence: Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Credit: The final interim report by the work group for studying the effects of the specific health checkups and specific health guidance on health care expenditures / The Work Group for Studying the Effects of the Specific Health Checkups and Specific Health Guidance on Health Care Expenditures ; Fukuda Takashi (work group member) [and 5 others] ; Hosurā Akiko (consultant). Source: Wellcome Collection.
23/260 (page 15)
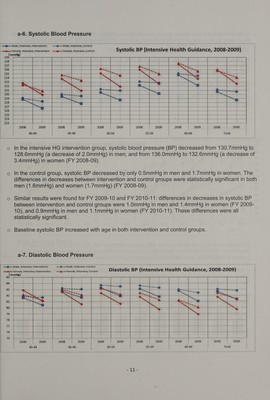
![—i— Male, Intensive, Intervention —t-— Female, intensive, Intervention — —® = Male, Intensive, Control te — Female, intensive, Control a GPT(ALT) {Intensive Health urdahes: 2008-2009) 45 - 40 = | } ee — 2 @-__ | | | | a : tsa | + | i | m~}---e 30 +— = ae L el] a. sie reed — | ieee | oT © ps Ons 25 = stam | . 2 —_h= — = = ~~ “al is +——4 | oe — | eS 2008 2009 2008 2009 | 2008 2009 2008 2009 2008 2009 2008 2009 40-44 45-49 50-54 55-59 60-64 Total o Inthe intensive HG intervention group, ALT decreased from 33.9U/L to 29.0U/L in men (a decrease of 4.9U/L), and from 26.0U/L to 22.3U/L in women (a decrease of 3.7U/L) (FY 2008-09). In the control group, ALT decreased by only 1.5U/L in men and 1.1U/L in women. The differences in decreases in ALT between intervention and control groups were statistically significant in both men (3.3U/L) and women (2.6U/L) (FY 2008-09). Similar results were found for FY 2009-10 and FY 2010-11: the differences in decreases in ALT between intervention and control groups were 2.3U/L in men and 1.7U/L in women (FY 2009-10), and 1.6U/L in men and 2.1U/L in women (FY 2010-11). These differences were all statistically significant. a-13. Y-GT (Y-GTP) — additional indicator 3 | a a 70 | =~0 | | | On~-} Wg 65 | =<~@ | ee 60 ) =i >. =~» —~ 55 | | ss al ir | | 45 | | | ! : | . | / } | | 40 + — | i | H . i + | i | === +===A an Pa | | | — 35 a ee oe 7% = = r & ———-. 30 ro | 20 ! 2008 2009 2008 2009 2008 2009 2008 2009 2008 2009 2008 2009 40-44 45-49 50-54 55-59 60-64 Total o Inthe intensive HG intervention group, Y-GT decreased from 64.5U/L to 57.0U/L in men (a decrease of 7.6U/L), and from 33.5U/L to 30.1U/L in women (a decrease of 3.4U/L) (FY 2008-09). a5 <](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b32222762_0023.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)