A dictionary of chemical solubilities : inorganic / by Arthur Messinger Comey.
- Comey Arthur Messinger, 1861-
- Date:
- 1896
Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: A dictionary of chemical solubilities : inorganic / by Arthur Messinger Comey. Source: Wellcome Collection.
Provider: This material has been provided by the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh. The original may be consulted at the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh.
446/544 (page 422)
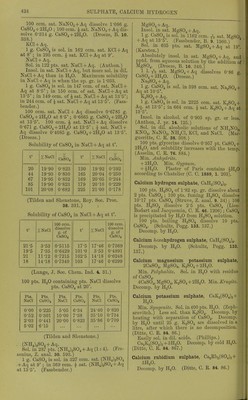
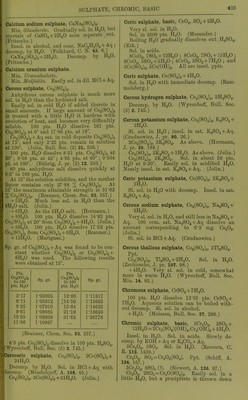
![dissolved part retains its water of crystallisa- tion. CaSOj, dehydrated at 130-140°, forms a supersaturated solution with HgO in 10 minutes containing 1 pt. CaSOj to 110 pts. H.,0, which soon deposits crystals. The undissolved part takes up its water of crystallisation. Ignited CaSOj dissolves very slowly in H.jO, so that in 24 hours the solution contains -^j^ to an- hydrous CaSOj. By longer contact solution continues with formation of supersaturated solutions, which contain after 10-30 days to ■sis CaSOj, but these become normal as the anhydrous CaS04 gradually takes up its water of crystallisation. The mineral anhydrite be- haves similarly, water taking up -j^j CaS04 in 1 day, g4^ in 40 days, and in 8 months. Supersaturated solutions are also obtained by evaporation of a saturated solution. By evajjoration with heat, solutions are obtained containing ^ CaSO^, and in the cold with xij- CaS04, in the solution over the separated CaS04-t-2H,0. Neutralising dil. HoSOj-l-Aq with CaCOg gives a .solution containing CaS04, which crystallises out partly in 24 hours, leaving CaSOj dissolved. Supersaturated solutions containing to xhs CaS04 dejiosit crystals rapidly; those under do not crystallise spontaneously. A solution containing tj-Itt shows crystals in 14 days, and contains ^hi 1 month, in 2 months, in 3 months, in spite of repeated shaking. Boiling diminishes the supersaturation with- out however removing it entirely. (Marignac, A. ch. (5) 1. 274.) 1 pt. CaS04-l-2H20 is sol. in 443 pts. H„0 at 13-7 ; in 447 pts. HgO at 14-2°; in 421 pts.'HgO at 20-2° ; in 419 pts. H„0 at 21-2°; and in 445 pts. HaCOs-t-Aq sat. at 18-7°. (Church, J. B. 1867. 192.) Church's solutions were not sat. (Droeze, B. 10. 330.) 1000 pts. HjO dissolve 2-19 pts. CaS04-t- 2H2O at 16-5°; 2-352 pts. CaS04-f 2H2O at 22°. (Cossa, Gazz. ch. it. 1873. 135.) Cossa's solutions were not saturated. (Droeze.) CaS04-)-2H,0 is sol. in 415 pts. H„0 at 0°; in 412 pts. H2O at 5°; in 407 pts. HjO at 10°; in 398 pts. H2O at 15°; in 371 pts. H,0 at 20°; in 365 pts. H2O at 25°; in 361 pts. H2O at 30°; in 359 pts. HjO at 35°. (Droeze, B. 10. 330.) Sol. in 500 pts. H2O at 12-5°. (From Marig- nac's and his own results, de Boisbaudran, A. ch. (5) 3. 477.) CaSOj is sol. in 564-5 pts. HjO at 0-8°; 506-27 pts. at 14°; 472-3 pts. at 32-5-38-8°; 498-73 pts. at 64°; 533-92 pts. at 79-6°. (Raupenstrauch, M. 6. 563.) According to Goldammer (C. C. 1888. 708) HoO is fully saturated with CaSOj by shaking the finely-powdered substance 5 minutes there- with. The following results were obtained. Figures denote pts. HgO in which 1 pt. CaSOj was dissolved at t° (a) from pptd. CaSOj ipse fact., (b) from pptd. CaS04 gelie, (c) from glacies mariac pulv., (d) from glacies mariae pulv., containing less than 2H2O. t° a b c t' (1 0 561-5 558 557-5 0 476-5 7 5 526 526 520 15 497-5 497-5 493 20 436 22-5 481 481-5 479 30 475 475 470 37-5 463 469 465-5 40 450 45 473-5 474-5 470-5 60 484 486-5 482 60 476 75 507-5 508 503 80 602-5 90 533-5 530 534 100 556 557 534-5 166 547 Burnt gypsum easily fonns supersat. solu- tions containing nearly 1 % CaSO. It fornu supersat. solutions more readily at 0°, and that tendency decreases with increase of temp., hence figures in (d) which contained biurnti gypsum. (Goldammer, C. C. 1888. 708.) Calculated from electrical conductivity ol CaSOj-f Aq, 1 1. H.fi dissolves 2-07 g. CaSOjali 18°. (Kohlrausch and Rose, Z. phys. Ch. 121 241.) Solubility of CaSOj in 100 pts. HjO at high temp. Pts. CaS04 t° Pts. CaS04 t° Pts. CaS04 140 165 0-078 0-056 175-185 240 0-027 0-018 250 0-016 (Tilden and Shenstone, Phil. Trans. 1884. 31.]. Solubility of CaS04 in HgO at various pres-> sures. 100 g. sat. CaS04-f Aq at 1 atmos. pressurai and 15^ contain 0-206 g. CaS04; at 20 atmos.N pressure and 15° contain 0-227 g. CaSOj; afei 1 atmos. pressure and 16-2° contain 0-213 g.^' CaS04. (MoUer, Pogg. 117. 386.) CaS04 is completely insol. in sea water or> pure H2O at temperatures between 140° andx 150°. (Coustd.) Solubility of CaSOj in sea water at temper-^ atures over 100. t° = temp. ; P = pressure-: in atmospheres ; % = per cent CaS04 in sat - solution. t° P % r P % 103 1 0-500 118-5 1-50 0-226 103-8 1 0-477 121-2 1-5 0-183 105-15 1 0-432 124 2 0-uo 108-6 1-25 0-395 127-9 2 0-097 111 1-25 0-355 130 2-5 0-060 113-2 1-25 0-310 133-3 2-5 0-023 115-8 1-50 0-267 (Couste, Ann. Min. (5) 6. 80.) Pptn. of CaS04 which has been started hy heating solution to 140-150° continues after solution has cooled. (Storer.) Sp. gi-. of sat. CaS04 + Aq at 15°-r002-2. (Stolba, J. pr. 97. 503.)](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b21713613_0446.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)