An atlas of the normal and pathological nervous systems : together with a sketch of the anatomy, pathology, and therapy of the same / Tr. and ed. (authorized) by Joseph Collins.
- Christofredo Jakob
- Date:
- 1896
Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: An atlas of the normal and pathological nervous systems : together with a sketch of the anatomy, pathology, and therapy of the same / Tr. and ed. (authorized) by Joseph Collins. Source: Wellcome Collection.
Provider: This material has been provided by the Augustus C. Long Health Sciences Library at Columbia University and Columbia University Libraries/Information Services, through the Medical Heritage Library. The original may be consulted at the the Augustus C. Long Health Sciences Library at Columbia University and Columbia University.
113/442 (page 43)
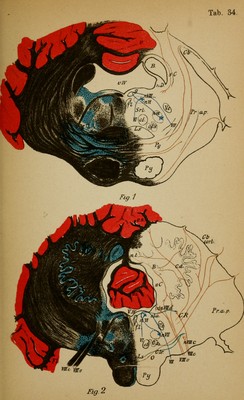
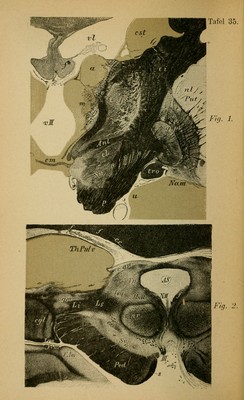
![Fig. 1.—Section through the Eight Optic Thalamus at the Level of the Middle Commissure. (Sloping somewhat obliquely posteriorly.) The three nuclei of the thalamus are easily recognized (nucleus anterior [a], medial [w], and lateral [/]). From the anterior there passes at this level a thick bun- dle (which in the horizontal section, Plate 31, is cut transversely [r] [Vic d'Azyr's bundle]) which ends in the corpus candicans of the same side (its course into the latter is well shown in the unstained section, Fig. 2, Plate 8). Beneath the thalamus lies the subthalamic region with the ansa lenticularis (Anl), Luys' body (cL), the fibres of which penetrate the internal capsule transversely and go to the globus pallidus (glp) of the lenticular nucleus; beneath the substantia nigra (Sn). In the lateral nucleus (trellis layer) the corona radiata passes out of the internal capsule (e i) into the thala- mus. The middle commissure (cm) contains but few nerve fibres. The medial nucleus forms posteriorly the pulvinar, in which ramify the fibres from the optic tract and the optic radiation (for other illustrations see Plate 27). Fig. 2.—Section through the Anterior Corpora Quad- rigemina of the Left Side. One recognizes the more detailed abundance of fibres than in Plate 32, 1. The lettering is the same as in that figure. In the lateral geniculate body (cgl) and also in the anterior corpora quadrigemina (cqa) end the innumer- able arborizations of the fibres of the optic nerve. In this vicinity the tract for the pupillary reflex must be sought (from here to the oculomotorius nucleus, N1II). Beneath the multitude of outgoing motor oculi fibres (III) begins the crusta (Ped) in the medial segment of which can be seen Spitzka's bundle ($) (which contains probably the central tract for the motor cranial nerves) passing from the crusta up to the tegmentum and later decussating in the median line. 43](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b2121752x_0113.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)