Notes on analytical chemistry : for students in medicine / by Albert J. Bernays.
- Albert Bernays
- Date:
- 1886
Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: Notes on analytical chemistry : for students in medicine / by Albert J. Bernays. Source: Wellcome Collection.
67/160 page 57
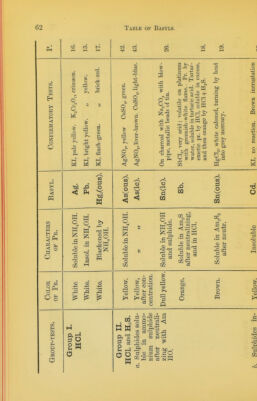
![silver oxide (brown-grey), eobaltous oxide, silver autimonide, an- hydrous cupric suliihate. [Many organic substances may be brown, yellowish, or grey, from impurity.] USUAL APPEAHANCES OP CRYSTALS. Transparent needles. Oxalic acid (also thicker and more opaque), magnesium, zinc, sodium, ammonium and quina sulphates, calcium chloride (deliquescent) urea, calcium sulphate (rather rare), ammonium nitrate, chloride, and oxalate, gallic acid (minute), sodium acetate, cupric chloride, hydrated ferric chloride (brown, deliquescent), soluble succinates, potassium picrate (yellow), urea oxalate, [thein, and many alkaloids.] Opaque needles. Hippuric acid, morphia, strychnia, magne- sium phosphate (minute), stannous chloride, lead acetate, mercuric and lead chlorides, potassium permanganate (dark purple), calcium benzoate, prismatic sulphur, potassiiun nitrate. Pearly or resinous lustre: (a) needles; silver acetate, alumininn sulphate, potassium ferricyanide. (/>) Plates or scales; benzoic acid and soluble benzoates, barium chloride, boracic acid, urea nitrate, potassium ferrocyanide (also massive square tables), barium hydrate, cadmium and lead iodides, chromic chloride (anhydrous, violet), potassium chlo- rate (?), [croton chloral, santonine, leucine, picric acid (also octahedra), some fatty acids, cholesterine, sebacic acid,] mercurous acetate. Short, thick crystals: («) efflorescent; most sodium salts, alums (octahedra), tartar emetic, cupric and ferrous sulphates, lead acetate, mercurous nitrate. (h) deliquescent; malic, phosphorous and phosphoric acids, zinc acetate, cadmium nitrate, hydropotassic sulphate. (c) permanent; potassium chromate, dichromate, hydro-car- bonate, sulphate, binoxalate, &c., tartaric and citric acids (if pure), strontium mtrate, calc-spar (CaCOs), Eochelle salt (sodiopotassic tartrate), sucrose, gypsum, &c. (d) opaque; plumbic nitrate (very marked), succinic acid, lactose, potassium hydrogen tartrate, mercuric cyanide, cinchonine salts. Cubes. Chlorides, bromides and iodides of alkaline metals (cjTinides usually in mass), iron pyrites, FeS^, galena, PbS, fluorspar', Lai 2. Potassium bromide is usually more transparent than the iodide. Substances commonly met with in masses, cakes, or lumps, fused salts generally, especially the following:— Structure pearly flakes: pure sodium and potassium hyd-](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b21499056_0067.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)