Volume 1
On the anatomy, physiology, and pathology of the chimpanzee / by Charles F. Sonntag.
- Sonntag, Charles F. (Charles Frederick), -1925
- Date:
- 1923
Licence: In copyright
Credit: On the anatomy, physiology, and pathology of the chimpanzee / by Charles F. Sonntag. Source: Wellcome Collection.
76/118 page 396
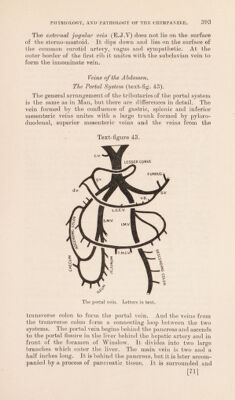
![The thymic constituent consisted mainly of concentric corpuscles and little lymphoid tissue. These conditions are, however, individual peculiarities. The thymus (text-fig. 42), lying in the thorax, consisted of a large left part reaching the level of the third costal cartilage, and a small right part reaching the second cartilage. These parts touched over the pericardium and the left part sent a process up under the great veins. Both parts have coarse lobules, and no cavity is present in either. It is supplied by the internal mammary artery, and the veins enter the left innominate vein. The spleen is small, measuring 3*8 ins. long, 2*4 ins. wide and T2 ins. thick. It has the same shape as in Man. The hilum is elongated. A small, oval accessory spleen is present. The artery is smaller than the hepatic artery. Other examples have larger spleens ; but the form and size depend on the stages in digestion. The suprarenal capsules are elongated bodies, with rounded ends, lying in the usual positions. They receive their arteries from the phrenic and renal arteries, but none from the abdominal aorta. The suprarenal plexuses are well marked. The Blood. Gulliver (23) pointed out that the red blood corpuscles have a diameter of 1/3412 inch, whereas those of Man are 1/3200 inch wide. The precipitin reactions have been described by Nuttall (38) who found that the blood of the Chimpanzee gives strong, positive reactions with those of Homo and Simla, but he does not mention its reaction with those of Gorilla and Hylobates. The Lymphatic System. The thoracic duct arises from a receptaculum chyli of con- siderable size by two vessels, which unite later. One vessel runs upwards on the right side of the thoracic aorta, and the other courses on the posterior surface of the oesophagus. At the level of the sixth dorsal vertebra the two vessels unite to form a trunk, which runs up between the oesophagus and vertebral column, and to the left side of the former. It then passes into the neck where it opens into the junction of the left subclavian and jugular veins. No right lymphatic duct was detected. The lymphatic glands are fewer than in Man, and the following groups were isolated :— A. Glands in the Head and, Neck:—1. A row of small glands lying on the surface of each submaxillary gland; 2. A group of both large and small glands between the cleido-mastoid and the larynx ; 3. No glands were found on the surface of the parotid or along the great vessels; 4. A group of glands over the sub- occipital region. [74]](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b2982123x_0001_0076.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)