On the analysis of the blood and urine, in health and disease. With directions for the analysis of urinary calculi / [George Owen Rees].
- George Owen Rees
- Date:
- 1836
Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: On the analysis of the blood and urine, in health and disease. With directions for the analysis of urinary calculi / [George Owen Rees]. Source: Wellcome Collection.
146/168 (page 132)
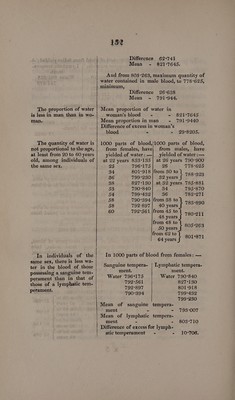
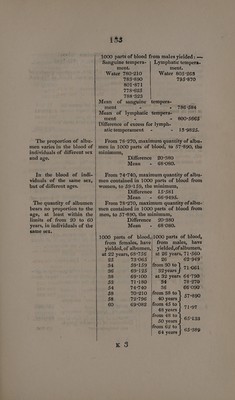
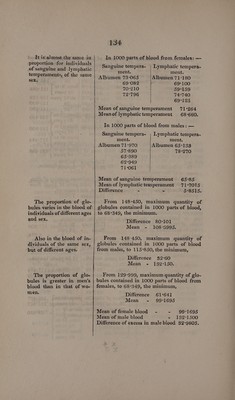
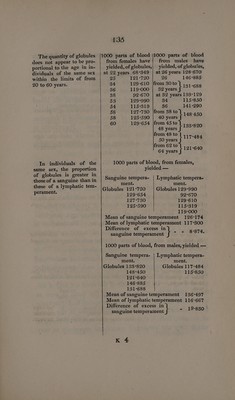
![The proportion of water is less in man than in wo- man. The quantity of water is not proportional to the age, at least from 20 to 60 years old, among individuals of the same sex. In individuals of the same sex, there is less wa- ter in the blood of those possessing a sanguine tem- those of a lymphatic tem- perament. 132 Difference 62°741 Mean - 821°7645. And from 805:263, maximum quantity of water contained in male blood, to 778°625, minimum, Difference 26-638 Mean - 791°944. Mean proportion of water in woman’s blood = - - 821°7645 Mean proportion in man - 791°9440 Difference of excess in woman’s blood - - 29°8205. 1000 parts of blood,/1000 parts of blood, from females, have| from males, have yielded of water: —| yielded of water :— at 22 years 853°135 | at 26 years 790°900 25 7T96°175 26 778°625 34 801°918 |from 30 to ao 86 799-230] 32 tales ePe oe 38 827°130] at 32 years 785°881 53 790°:840 34 795°870 54 799:432 36 782°271 58 790°394 |from 38 to 58 792°897{| 40 years T85920 60 792°561 |from 45 to 48 years f 780°211 from 48 to be na 805°263 from 62 to saya 801°871 In 1000 parts of blood from females: — Sanguine tempera- | Lymphatic tempera- ment. ment. Water 796°175 Water 790°840 792°561 827°130 792°897 801°918 790°394 799°432 799°230 Mean of sanguine tempera- ment - - 793:007 Mean of lymphatic tempera- ment - - 803-710 Difference of excess for lymph- atictemperament - - 10°708.](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b33095127_0146.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)