Internal secretion and the ductless glands / by Swale Vincent ; with a preface by E.A. Schäfer.
- Vincent, Swale, 1868-1934.
- Date:
- 1922
Licence: In copyright
Credit: Internal secretion and the ductless glands / by Swale Vincent ; with a preface by E.A. Schäfer. Source: Wellcome Collection.
51/452 (page 27)
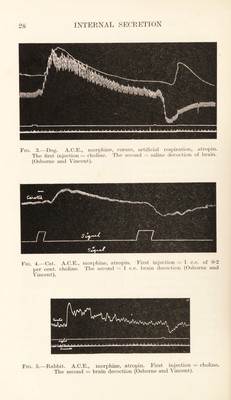
![extracted, not only from nervous tissues, but also from all kinds of muscular tissue, kidney, liver, spleen, testis, pancreas, ovary, and lung. They note, also, that other observers have extracted a depressor substance from thyroid, thymus, adrenal, and pituitary body. Pigs. 6 and 7 show the effect of injection of ex¬ tracts of muscle. Pig. 8 shows the effect of brain extract for the purpose of comparison. By this time it had become tolerably clear to the present writer that all animal tissues impart to watery or saline extracts a substance or substances which, when injected into the circulation of a living animal, affect the arterial blood-pressure. The effect produced by these sub¬ stances is depressor, with the exception of the medulla of the adrenal [‘‘ paraganglion supra¬ renale” (Kohn)], other groups of chromaphil cells, and the infundi¬ bular portion of the pituitary body. It had also been rendered prob¬ able that these depressor effects of an extract are not to be regarded as an indication of an internal secretion on the part of the tissues in question. This seems now to be generally recognized, and the view is adopted in the majority of textbooks. It is naturally of some interest and importance to ascertain Fig. 2.—Dog. A.C.E., morphine, curare, artificial respiration. Hind -limb pletbysmograph. Hooks in auricle and ventricle. Injection of 2 c.c. saline decoction spinal cord (Osborne and Vincent).](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b29928928_0051.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)