The development of the human body : a manual of human embryology / by J. Playfair McMurrich.
- McMurrich J. Playfair (James Playfair), 1859-1939.
- Date:
- 1910
Licence: In copyright
Credit: The development of the human body : a manual of human embryology / by J. Playfair McMurrich. Source: Wellcome Collection.
Provider: This material has been provided by the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh. The original may be consulted at the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh.
483/546 (page 469)
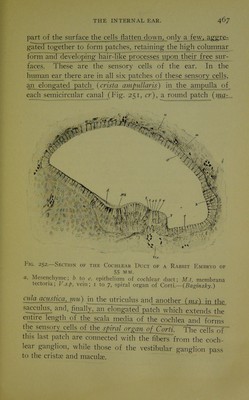
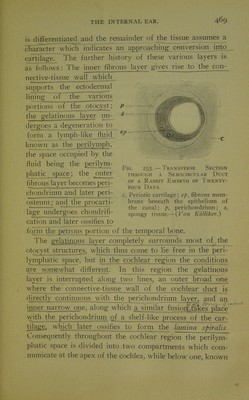
![is differentiated and the remainder of the tissue assumes a character which indicates an approaching conversion into cartTlage. The further history of these various layers is as follows: The inner fibrous layer gives rise to the con- nective-tissue wall which supports the ectodermal lining of the various Fig. 253. — Transverse Section THROUcai A Semicircular Duct OF A Rabbit Embryo of Twenty- four Days. c, Periotic cartilage; e[>, fibrous mem- brane beneath the epithelium of the canal; p, perichondrium; s, spongy tissue.— {Von Kdlliker.) portions of the otocyst; the gelatinous layer un- dergoes a degeneration to form a lymph-like fluid known as the 2?nl;^^i.n]2l3» the space occupied by the fluid being the perilym- phatic _s2ace^; the outer fibrous layer becomes peri- chondrium and later peri- osteum; and the procarti- lage undergoes chondrifi- cation and later ossifies to ionn the petrous jportion of the temporal bone. The gelati^),9us layer completely surrounds most of . the otocyst structures^, which thus come to lie free in the peri- lymphatic space, but in the cochlear region the conditions are somewhat different. In this region the gelatinous layer is interrupted along two lines, an outer broad one \vhere the connective-tissue wall of the cochlear duct is (lirectly continuous with the perichondrium layer, and an - inner narrow one, along which a similar fusioi-f^^es place vvith the perichondrium of a shelf-like process of the car- tilage, which later ossifies to form the lamina spiralis. Consequently throughout the cochlear region the perilym- phatic space is divided into two compartments which com- municate at the apex of the cochlea, while below one, known](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b21713145_0483.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)