World survey of pest control products / by Laura G. Arrington.
- United States. Business and Defense Services Administration. Chemical and Rubber Division.
- Date:
- [1956]
Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: World survey of pest control products / by Laura G. Arrington. Source: Wellcome Collection.
13/228 (page 3)
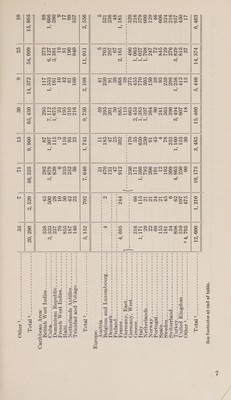
![However, these figures do not give a complete picture of pesticide production. It has been estimated that manufacture of all basic pesticide toxicants (not including formulations) at the manufacturers level was valued at $160 million in 1953, $175 million in 1954, and probably will top $190 million in 1955. (For statistics on output of individual pesticide materials in recent years see table 1.) Consumption The use of pesticides is increasing not only in volume but in variety, and application of specialized products for specific controls is becoming more general. In number of compounds available for control of various insects, fungi, weeds, and the like the pesticide field has expanded more in the past 10 years than during all previous years of its history, and the list is ever increasing. Constant research is being conducted, both by government agencies and private corpora- tions, to discover and test chemical compounds for effectiveness as insecticides, fungicides, weedkillers, and other purposes, particularly for specific controls. Only within recent years have such materials as defoliants been used on plants such as cotton, potatoes, and soy beans. Selective weedkillers have come into common use only within the past decade, particularly on small grains. Pre-emergence weedkillers also are becoming popular. Use of herbicides not only increases output per acre, but reduces the number of man-hours required for a unit of production, thus alleviating to some degree the shortage of farm labor. A rapidly growing market for pesticides lies in protection of stored grain. The United States Department of Agriculture and the Food and Drug Administration, United States Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, are uniting forces in this project which will save thousands of tons of grain as well as provide the public with noninfested cereal products. 2 ie] Also, for control of livestock pests, there are a number of new materials, use of which results in added weight of beef cattle and hogs and increases milk production. Use of various new organic insecticides has been a big factor in control of flies and other house- hold insects, as well as in lessening infestations around barns, dairies, and other outbuildings. | Through cooperation of the United States Public Health Service and State and municipal authorities, incidence of malaria has been practically eradicated in the United States. Furthermore, United States Government and municipal authorities have cooperated on a number of successful rat-eradication programs. Table 2 gives domestic disappearance of some major agricultural pesticides in recent crop years. However, these statistics do not take into consideration the ever-growing use of newer commodities,](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b32176740_0013.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)