The animal parasites of man : a handbook for students and medical men / by Max Braun.
- Braun, Max (Maximilian Gustav Christian Carl), 1850-1930.
- Date:
- 1906
Licence: In copyright
Credit: The animal parasites of man : a handbook for students and medical men / by Max Braun. Source: Wellcome Collection.
431/488 (page 407)
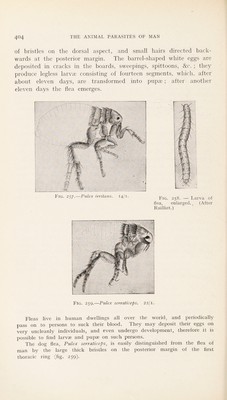
![5. Pulex fasciatus, Bose. This flea is also found on the rat and will attack man. It has eighteen teeth on the prothoracic comb and no black spines on the head. 6. Pulex pallipes is another species found on the rat and man. 7. Typhlopsylla musculi, Duges (The Rat Flea). In the genus Typhlopsylla the body is narrow and elongated, and on the under side of the head are numerous chitinous bristles, and also on the pronotum. This rat flea is also found on the vole ; it is dark yellowish-brown and the body attenuated in front, and there is a distinct comb on the posterior margin of the pro- notum ; the legs have very few hairs, femora bare and curved ; tibiae with black bristles ; four spines on the genae. An allied species, T. assimilis, Taschenberg, occurs on mice, shrews, moles, and voles ; it has only three genal spines.—F. V. T.] Systematic, AxNAtomical, and Biological Remarks on Mosquitoes. Mosquitoes Nematocera form one of the four sub-orders of the Diptera, and are divided into numerous families, of which, however, only the CulioidcB are of interest to us here. The head is small, the facetted eyes are placed laterally, but there are no accessory eyes (ocelli). In front of the eyes are situated the comparatively long antennae, the differences of which strongly mark the distinction of sex.' The antennae are composed of hfteen or sixteen segments. In the male they are covered with long whorl-like hairs, while in the female the antennal hairs are short—-differences that are perceptible even with the naked eye.^ The proboscis, which is longer than the antennae, protrudes from the inferior aspect of the head and is composed of the following parts (figs. 264 and 265) : Two grooved half tubes, facing one another, of which the upper one is the upper lip (labium), and the lower one the lower lip (labrum), which represents a pair of coalesced maxillae. Within the tube formed by the labrum and labium are the mandibles and maxillae, transformed into instru- ments for piercing, and a single puncturing organ, the hypopharynx. On the right and left, next to the proboscis, are placed the straight five- ’ [This is by no means always the case ; in the genera Deinocerites, Wyeomyia, Limatus, Theobald, and in Sahethes, Robineau Desvoidy, they are nearly the same in both sexes.—F. V. T.] ' [This is not always the case, vide previous note.—F. V. T.l](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b29004755_0431.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)