The animal parasites of man : a handbook for students and medical men / by Max Braun.
- Braun, Max (Maximilian Gustav Christian Carl), 1850-1930.
- Date:
- 1906
Licence: In copyright
Credit: The animal parasites of man : a handbook for students and medical men / by Max Braun. Source: Wellcome Collection.
437/488 (page 413)
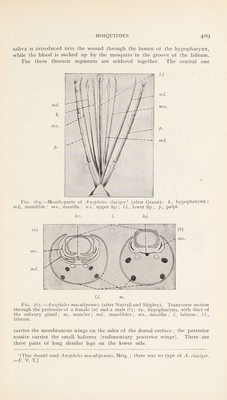
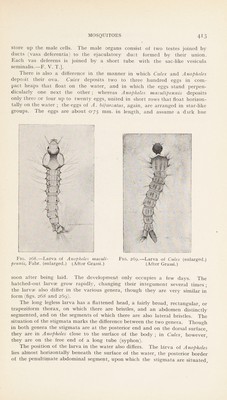
![store up the male cells. The male organs consist of two testes joined by ducts (vasa deferentia) to the ejaculatory duct formed by their union. Each vas deferens is joined by a short tube with the sac-like vesicula seminalis.—F. V. T.]. There is also a difference in the manner in which Culex and Anopheles deposit their ova. Culex deposits two to three hundred eggs in com- pact heaps that float on the water, and in which the eggs stand perpen- dicularly one next the other; whereas Anopheles maculipennis deposits only three or four up to twenty eggs, united in short rows that float horizon- tally on the water ; the eggs of A. bifurcatus, again, are arranged in star-like groups. The eggs are about 0'75 nim. in length, and assume a dark hue Fig. 268.—Larva of Anopheles maculi- Fig. 269.—Larva of Culex (enlarged.) pennis, Fahr, (enlarged.) (After Grassi.) (After Grassi.) soon after being laid. The development only occupies a few days. The hatched-out larvae grow rapidly, changing their integument several times ; the larvae also differ in the various genera, though they are very similar in form (figs. 268 and 269). The long legless larva has a flattened head, a fairly broad, rectangular, or trapeziform thorax, on which there are bristles, and an abdomen distinctly segmented, and on the segments of which there are also lateral bristles. The situation of the stigmata marks the difference between the two genera. Though in both genera the stigmata are at the posterior end and on the dorsal surface, they are in Anopheles close to the surface of the body ; in Culex, however, they are on the free end of a long tube (syphon). The position of the larva in the water also differs. The larva of Anopheles lies almost horizontally beneath the surface of the water, the posterior border of the penultimate abdominal segment, upon which the stigmata are situated.](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b29004755_0437.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)