An introduction to human physiology / by Augustus D. Waller.
- Waller, Augustus.
- Date:
- 1896
Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: An introduction to human physiology / by Augustus D. Waller. Source: Wellcome Collection.
Provider: This material has been provided by University of Bristol Library. The original may be consulted at University of Bristol Library.
121/678 (page 103)
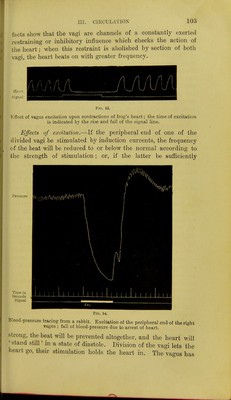
![facts show that the vagi are channels of a constantly exerted restraining or inhibitory influence which checks the action of the heart; when this restraint is abolished by section of both vagi, the heart beats on with greater frequency. Ill' /1 f\ /'I [\ /] fjm. Fig. 63. Effect of vagus excitation upon contractions of frog's heart; the time of excitation is indicated by the rise and fall of the signal line. Effects of excitation.—If the peripheral end of one of the divided vagi be stimulated by induction currents, the frequency f)f the beat will be reduced to or below the normal according to the strength of stimulation; or, if the latter be sufficiently Pressure Time in Seconds Signal Fig. 54. Blood-pressure tracing from a rabbit. Excitation of the peripheral end of the right ▼agUB ; fall of blood-pressure due to arrest of heart. strong, the beat will be prevented altogether, and the heart will ' stand still' in a state of diastole. Division of the vagi lets the heart go, their stimulation holds the heart in. The vagus has](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b21443981_0121.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)