On the proportion of nitrogen contained in alimentary substances taken from both the organic kingdoms as a comparative measure of their nutritive power.
- Schlossberger, J., Dr.
- Date:
- [1845]
Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: On the proportion of nitrogen contained in alimentary substances taken from both the organic kingdoms as a comparative measure of their nutritive power. Source: Wellcome Collection.
Provider: This material has been provided by The Royal College of Surgeons of England. The original may be consulted at The Royal College of Surgeons of England.
11/12 (page 11)
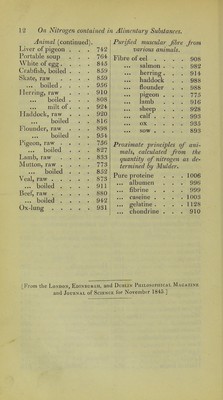
![be inferior to one with a much smaller quantity as regards the nourishing effects produced by it; if in the first of these cases only a pai't, in the second the whole may be easily absorbed and assimilated. Here we must rely upon the experiments of the physiologist as to the degree of digestibility of different substances; and there already exists an excellent basis in the researches of Beaumont and of Blondlot. This is one of the questions, in which, by the co-operation alone of the physio- logist and chemist, any progress can be expected to be made in the elucidation of this point. If the work wereonce fairly begun by the physiologist, chemistry would not be long in rendering that assistance which would then be found neces- sary; for example, in the various experiments which might be made in artificial digestion, from the results of which as one element in the calculation taken along with the proportion of nitrogen as the other, it would at once be possible to deter- mine scientifically the real nutritive value of the different kinds of aliment; the importance to our dietetics of this method of determination, which at present exists only in idea, would then not only be felt by the patient, but by the whole human race. Table of the comparative proportion of nutriment in our organic aliments. If we assume the amount of nitrogen in human milk, perfectly dried at 212° F., to be represented by 100, we can then express the degree of nutritive power of the other alimentary substances by the following numbers:— Vegetable. Agaricus deliciosus . 289 Rice 81 Beans .... Potatoes 84 Turnips 106 A nimal. Rve 106 Human milk . . 100 Maize . . . . 100 to 125 Cow’s milk . 237 Barley 125 Oyster .... . 305 Unfermented bread of Yolk of egg . . 305 Glasgow .... 134 Cheese. . . .331 to 447 Oats 138 Eel, raw . . . 434 White bread .... 142 ... boiled . 428 Wheat . . . . 1 ] 9 to 144 Liver of crabfish . 471 Carrots 150 Mussel, raw . . 528 Brown bread .... 166 ... boiled . . 660 Agaricus cantharellus . 201 O.x-liver, raw. . 570 Peas 239 Pork-ham, raw . . 539 Agaricus russula . . 264 ... boiled . 807 Lentils 276 Salmon, raw . . 776 Haricot beans . . . 283 ... boiled . . 610](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b22469424_0013.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)