Observation in medicine, or, The art of case-taking : including a special description of the most common thoracic diseases, and abnormal states of the blood and urine / by John Southey Warter.
- Warter, John Southey.
- Date:
- 1865
Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: Observation in medicine, or, The art of case-taking : including a special description of the most common thoracic diseases, and abnormal states of the blood and urine / by John Southey Warter. Source: Wellcome Collection.
80/140 (page 60)
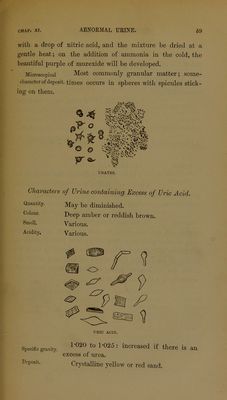
![CHAP. XI. Chemical elm- A deposit of uric acid is insoluble when raeters of deposit, the urine is heated; it is soluble in alkalies, and if the solution is again rendered acid uric acid crystals are deposited ; treated with nitric acid and ammonia, the deposit gives the purple of murexide (see Urine containing Excess of Urates). Microscopical Lozenge-shaped crystals, and irregular examination of striated masses, often stained dirty yellow deposit. brown. Characters of Urine containing Excess of Uroxanthine [Indie ari]. Acidity. Colour (?). Persistent and marked. I have generally noticed the colour to be a pale straw yellow, the phosphates or urates precipitated being colourless. Deposit (?). White urates or phosphates. Chemical If the urine be floated on to one-third of characters. its volume of sulphuric acid (specific gravity 1-830), and the two fluids be then gradually mixed; tints from a faint pink to a deep indigo blue show themselves, indicating the amount of uroxanthine present by their in- tensity of colour (the tube should be kept cool while the fluids are mixing, by gently shaking it when immersed vertically in a basin of cold water).](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b28106428_0080.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)