Normal histology : a manual for students and practitioners / by John R. Wathen.
- Wathen, John Roach, 1872-
- Date:
- [1905]
Licence: In copyright
Credit: Normal histology : a manual for students and practitioners / by John R. Wathen. Source: Wellcome Collection.
68/232
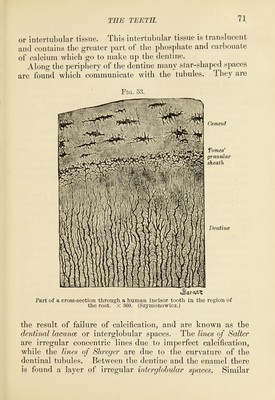
![spaces, hut smaller, are fouiul between the cementiim and the dentine ; these latter being called Tonies^ granular layer. The pulp, which occupies the cavity surrounded by the dentine, consists of a matrix of immature connective tissue with many stellate and spindle cells, nerves, and bloodvessels. AVhere the pulp comes into contact with the dentine are layers of elongated connective-tissue cells, lying perpendicular to the dentine and known as odontoblasts. These cells send processes into the dentinal tubules, known as the dentinal fibres. The bloodvessels and nerves supplying the pulp break up to form plexuses which are found under the odontoblasts. The nerves enter the pul])-cavity and pass up through its centre, with numerous branches running toward the periphery, and lose their medullary sheath as they pass up among the odontoblasts, ending as small swellings between the dentine and these cells. The enamel is formed of a number of six-sided prisms, composed of a very dense, hard substance containing little organic matter. These columns or prisms are not straight, but present wavy borders, run through the entire thickness of the enamel, and are held together by a delicate layer of cement. A delicate but resistant membrane, known as the enamel cuticle or memhi'ane of Nasmyth, which is the remains of the enamel organ, covers the external surface of the enamel, and remains for a short time after birth. The cementum, or crusta petrosa, surrounds the fang of the tooth from the end of the enamel to. the apex of the fang, and closely resembles bone, being made up of parallel laniellse or layers of bone-tissue containing lacun^e. Haver- sian canals are very rarely found. This cementum is in direct contact with a vascular fibrous structure similar to the ]^criosteum of bone, called the periodontal membrane, of wliich it is the product. Unlike the })ulp, the dentine is a tissue entirely free from bloodvessels and nerves. The cementum is non-vascular, and the enamel may be considered as a dead substance which needs no nourisliment. Development of the Teeth.—The enamel of the teeth is](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b2805801x_0068.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)