Affinity labelling and cloning of steroid and thyroid hormone receptors / edited by H. Gronemeyer.
- Date:
- [1988]
Licence: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
Credit: Affinity labelling and cloning of steroid and thyroid hormone receptors / edited by H. Gronemeyer. Source: Wellcome Collection.
309/332 (page 305)
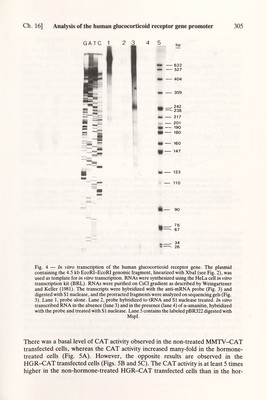
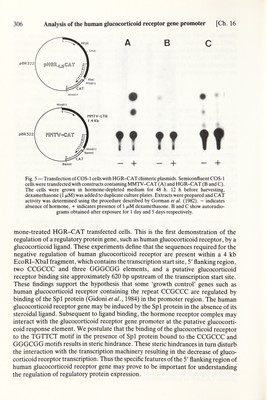
![Ch. 16] Analysis of the human glucocorticoid receptor gene promoter 305 IMH > к — 110 Fig. 4 — In vitro transcription of the human glucocorticoid receptor gene. The plasmid containing the 4.5 kb EcoRI-EcoRI genomic fragment, linearized with Xbal (see Fig. 2), was used as template for in vitro transcription. RNAs were synthesized using the HeLa cell in vitro transcription kit (BRL). RNAs were purified on CsCl gradient as described by Weingartener and Keller (1981). The transcripts were hybridized with the anti-mRNA probe (Fig. 3) and digested with SI nuclease, and the protracted fragments were analyzed on sequencing gels (Fig. 3). Lane 1, probe alone. Lane 2, probe hybridized to tRNA and SI nuclease treated. In vitro transcribed RNA in the absence (lane 3) and in the presence (lane 4) of a-amanitin, hybridized with the probe and treated with SI nuclease. Lane 5 contains the labeled pBR322 digested with MspL There was a basal level of CAT activity observed in the non-treated MMTV-CAT transfected cells, whereas the CAT activity increased many-fold in the hormone- treated cells (Fig. 5A). However, the opposite results are observed in the HGR-CAT transfected cells (Figs. 5B and 5C). The CAT activity is at least 5 times higher in the non-hormone-treated HGR-CAT transfected cells than in the hor-](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b18029310_0310.JP2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)