Tropical hygiene for residents in tropical and sub-tropical climates / by Pardy Lukis and R.J. Blackham.
- Lukis, Charles Pardey, Sir, 1857-1917.
- Date:
- 1915
Licence: In copyright
Credit: Tropical hygiene for residents in tropical and sub-tropical climates / by Pardy Lukis and R.J. Blackham. Source: Wellcome Collection.
Provider: This material has been provided by London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine Library & Archives Service. The original may be consulted at London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine Library & Archives Service.
317/332
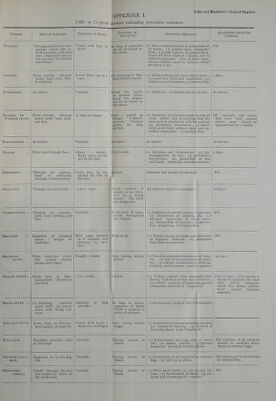
![-APPENDIX I. Tabic oj Tropical diseases indicating 1. preventive measures. ukis and Blackham*s Tropical Hygiene. Disease. Mode of lufectiou. Duration of Illness. Duration of Infectivity. Preventive Measure^ Quarantine Period for Contacts. Malaria Through another Hue mos- quitoes which bite in- fected persons, and some time afterwards convey the parasite to healthy individuals. Varies with type of fever. So long as parasites are to be found in the blood. (i) Aim at extermination of mosquitoes of all kinds ; (2) protect from mosquito- bites ; (3) take 5 grains of quinine daily. There are three types of malaria, due to different parasites. Two of these varie- ties are readily cured by quinine, whilst the third is not. j Nil. Cholera From excreta, through water, food, dust, flies, or clothing. A few hours up to 5 days. Till discharge is free 1 from cholera bacilli. (I) Drink nothing but tea or boiled water ; (2) avoid raw fruits and vegetables ; (3) sulphuric acid lemonade; (4) destroy flies. 5 days. Dysentery As enteric .. Variable Whilst the bacilli ' or aniosba^ which | cause the disease 1 are to be found in 1 the stools. ' 1 (i) Isolation ; (2) disinfection of! excreta . As enteric. Enteric or Typhoid fever. From excreta, through water, milk, food, dust, and flies. 21 days or longer . , From I month or longer. Typhoid- 1 carriers harbour germs for long periods. (1) Isolation ; (2) disinfect most strictly all urine, stools, arid everything'that has been used in connection with the patient; (3) preventive inoculation ; (4) habit- ually avoid food without skins and un- cooked vegetables ; (5) destroy flies. 1 All contacts and nurses who have been nursing enteric cases should be quarantined for a month. Paratyphoid .. As enteric .. Variable As enteric As enteric . . .. As enteric. Plague From rats through fleas . About I month. Many cases di eon 3rd to 5th day. (3 to S weeks (i) Isolation and disinfection;; (2) dis- couragement of rats ; (3) preventive inoculation ; (4) protectioni of feet and hands, especially abraided surfaces. 1 5 days. Pneumonia Through air, sputum, food or indirectly through a third person. Crisis may be ex- pected on 6th to 8th day. 24 days Isolation and careful disinfection Nil, Small-pox Through air and breath. . 14 to 21 days About I month. A corpse is as infec- tive as a living person. The dead are dangerous. AH contacts must be vaccinated 16 days. Tuberculosis . Through air, sputum, milk, food, clothing, and flies. Variable In tubercle of lung ; exists throughout 1 the disease. 1 {I) Isolation of infected person, if possible; (2) disinfection of clothing, etc. ; {3) efficient inspection of milch cows ; (4) disinfection of sputum ; (5) preven- tion of spitting ; (6) banish flies. Nil. Pellagra Ingestion of diseased maize ; ? midges or sand-flies. Mild cases recover in 6 months, but recovery is very rare. None at all (I) Proper drying of maize and of hygienic bakeries ; (2) from bites of sand-flies. provision )rotection Nil. Relapsing FEVER. From body-lice which bite person, during paroxysmal stage. Usually 3 weeks Only during febrile period. (I) Maintain complete cleanliness of room, etc. ; (2) aim at extermination of body- lice ; (3) careful disinfection of clothing, bedding, and furniture, used by patient. 14 days. Yellow fever . From bites of tiger- mosquitoes {Stegomyia fasciata). I to 2 weeks 4 weeks (i) Protect patient from mosquito-bites during first three or four days of illness ; (2) enforce carefully all nieasures against mosquitoes detailed in Chapter II. 8 to 12 days. This period is meant to indicate the time after which mosquito which has bitten yellow- fever patient becomes infective. Malta fever ,. (i) Drinking infected goat's milk ; (2) inocul- ation with living cul- tures. Extends to long periods. So long as micro- organism of Malta Fever is present in urine of patients. (i) Avoid goat's milk or boil it thoroughly Sand-fly fever From bites of Phleboto- mus variety of sand-fly. Varies with types a week to a fortnight. Only during febrile stage. (I) Protection by fine gauze mos (2) improved housing; (3) breeding-places {vide Chapter quito-nets cmoval 0 11). Kala-azar Doubtful, possibly bites of bed-bugs Variable During course of illness. (r) Exterminate bed-bugs and life ; {2) isolate patient ; migration of sick to healthy ] all insed 3) prevent )|aces. The clothing of all contacts should be carefully disin- fected to destroy bugs. Infantile kala- azar. Supposed to be the dog- flea. Variable During course of illness. (i) Destruction of all suspected dogs ; (2) and (3) as above. cr infectec The clothing to be disinfected to destroy fleas. Hookworm DISEASE. Chiefly through the feet and ankles by larvte of the hookworm. Variable During course of illness. (1) Wearing of boots; (2) use c rines ; (3) incineration of stoo lation and treatment of '* carr f pail lat- s ; (4) iso- ers. Nil. i](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b21360224_0319.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)