Hand atlas of human anatomy / by Werner Spalteholz ; translated from the 3rd German edition by Lewellys F. Barker.
- Spalteholz, Werner, 1861-1940. Handatlas der Anatomie des Menschen. English
- Date:
- 1900-
Licence: In copyright
Credit: Hand atlas of human anatomy / by Werner Spalteholz ; translated from the 3rd German edition by Lewellys F. Barker. Source: Wellcome Collection.
25/896 (page 13)
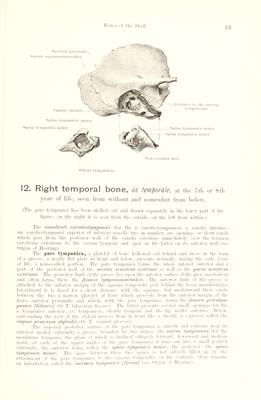
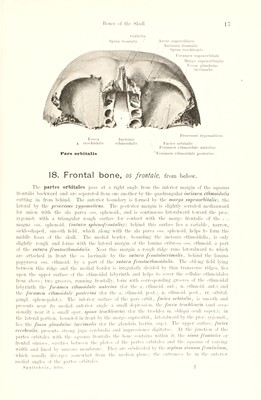
![I*'’Hi's of thi' Skull. Non - ossified area Canalis facialis — spina tympanica minor Spina tympanica major _Spina tympanica major Spina tympanica minor Incisura pariotalis^ Sutura squamosomastoidca \ A Sulcus tympanicus 12. Right temporal bone, os toniporolB, at the 7th or sth year of life, seen from without and somewhat from below. (The pars tympanica has been shelleil out and drawn separately in the lower part of the figure; on the right it is seen from the outside, on the left from within.) The canaliculi caroticotympanici (for the r. caroticotvmpanicus a. earotis internae: nn. caroticotympanici superior ot inferior) usually two in number, are openings or short canals which pass from the posterior wall of the canalis camticus immediately over the foramen caroticum externum to the cavum tympani and open in the latter on its anterior wall (see Organ of Hearing). The pars tympanica, a platelet of hone hollowed out behind and above in the form of a groove, a nearly flat plate in front and below, presents normally, during the early years of life, a non-ossified portion. The pars tympanica forms the whole inferior anterior and a part of the posterior wall of the meatus acusticus externus as well as the poms acusticus externus. The posterior limb of the groove lies upon the anterior surface of the proe. mastoideus and often forms there the fissura iympanomastoidea. The anterior limb of the groove is attached to the inferior margin of the squama temporalis just behind the fossa mandibularis; lateralward it is fused for a short distance with the sijuama. but median ward there exists between the two a narrow platelet of hone which proceeds from the anterior margin of the facies anterior pyramidis and which, with the pars tympanica, forms tlm [issuru petrotym- panica [GInsert/ (0. T. Glaserian fissure). The latter presents several small openings lor the a. tympanica anterior, vv. tvinpanicae, chorda tympani and the lig. mallei anterius. Helow, surrounding the root of the stvloid process from in front like a sheath, is a process called the vagina processus siyloulei (O. T. vaginal jiroeess). The superior posterior surface of the pars tympanica is smooth and contains near its anterior medial extremitx a groove, hounded I»v two ridges, the sulcus tympanums (tor the memhrana tvinpani), the plane of which is inclined obliquely lorward, downward and median- ward: at each of the upper angles of the pars tympanica it runs out into a small pointed extremity, the anterior being called the spina tympanica major, the posterior, the spina tympanica minor. The space between these two spines i.- not entiivlx filled up I',' the attachment of the pars tvmpaniea to the sipiama temporalis: on the eontrirx . there remains an indentation called the incisura tympanica [liiciui] (see Organ ol Haringi.](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b29336211_0025.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)