Annual report of the Director of Public Health for the Government of Bombay.
- Bombay (India : State). Public Health Department.
- Date:
- [1935]
Licence: Public Domain Mark
Credit: Annual report of the Director of Public Health for the Government of Bombay. Source: Wellcome Collection.
34/250 (page 18)
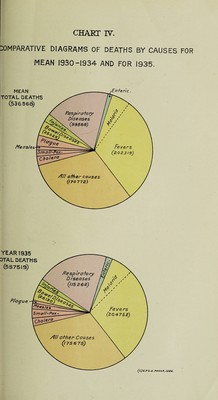
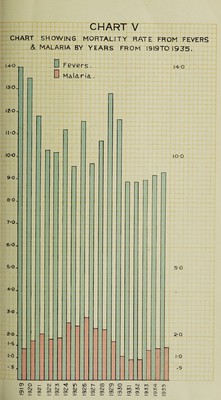
![39. Death-rates from fevers in TJrhan and rural areas.—High death- rates were recorded in the Presidency proper in the following towns Yiramganm (27*79), Nadiad (22*23), Mehmedabad (21*36), Ankleshwai (19*28), Umreth (18*34), Anand (17*07), Dohad (16*80), Borsad (15*16), Bander (15*06), and in Sind Batodero (14*00), Garhi Yasin (12*62), Matiari (8 * 96), Kambar (8*95) and Umarkot (8 * 08), In rural circles high death-rates were recorded in Edlabad (23*07), Amalner (20*69) Parola (20*62), Jalgaon (20*56) and Mulshi (20*49). Details of deaths from fevers are shown below :— Malaria.—ifVide Chapter VIII). 40. Enteric Fever.—The number of deaths from fevers registered as due to enteric was 7,041 against 6,684 in 1934, the ratio being *32 and *31 respectively. Enteric Fever is increasing in the. Presidency ; th( increase is due partially to better diagnosis of the disease but shar| outbreaks in several localities show’ the need of systematic investigation 41. Deaths from_ Enteric fever in urban and rural areas.—The numbej of deaths recorded from enteric fever in urban areas where the diseas< was more prevalent is as follows :—Sholapur 123, Poona City 100, Sura 82, Hubli 71, Hyderabad 69, Nasik 46, Karachi 43, Larkana 39, Sukkuj 34, Ilkal 31, Thana 30 and Bandra 28. In Bombay City 225 death.!; were recorded as compared with 235 in 1934. In Karachi City anti-63 measures were adopted throughout the year and T. A. B. inoculation! offered free of charge in the Municipal Dispensaries. The number 0 deaths recorded under this head for the rural areas in the districts when the disease was prevalent is as follows :—Kolaba 872, West Khandesl 853, Thana 588, Nasik 516, Ahmednagar 472, Dharwar 440, Kanara 417 and Belgaum 332. j 42. Measles.—The number of deaths registered as due to measlej was 8,463 against 2,816 in 1934. The death-rate was *39 against *1<‘ in the previous year. The urban death-rate was *61 and the rura *33. 43. Deaths from Measles in urban and rural areas.—High death rates for urban areas were recorded in Bagalkot (3*64), Umreth (3*59) Nandurbar (3 * 43), Mehmedabad (3 * 37), Malegaon (3 * 33), Gadag (3 * 18) Parola (3*01), Sholapur (2*99), Chalisgaon (2*97) and Dharangao] (2*16). In Bombay City 264 deaths were recorded as against 158 h 1934. The number of deaths from Measles in rural areas of the district where the disease was most prevalent is as follows :—AVest Khandes] 1,637, Belgaum 834, Satara 625, Nasik 571, East Khandesh 532, Dharwa 324 and Bijapur 276. The disease was considerably severe during th year since 1929 when 8,853 deaths were recorded. 44. Relapsing fever.1—No death wTas recorded under this head during the year. 45. Kola Azar.—One death from Kala Azar was reported frou Bombay City during the year. The Executive Health Officer, Bomba j Municipality, reports in connection with this case:—“ The patient (male;](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/b31405319_0034.jp2/full/800%2C/0/default.jpg)