Kate Turner, Dr Steve Wilson
Works from the collections
12 works
- Digital Images
- Online
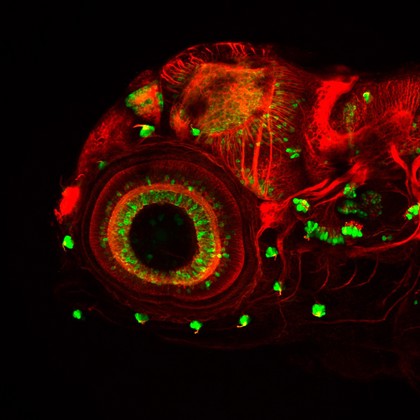
Eye development, zebrafish
Kate Turner, Dr Steve Wilson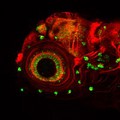
- Digital Images
- Online
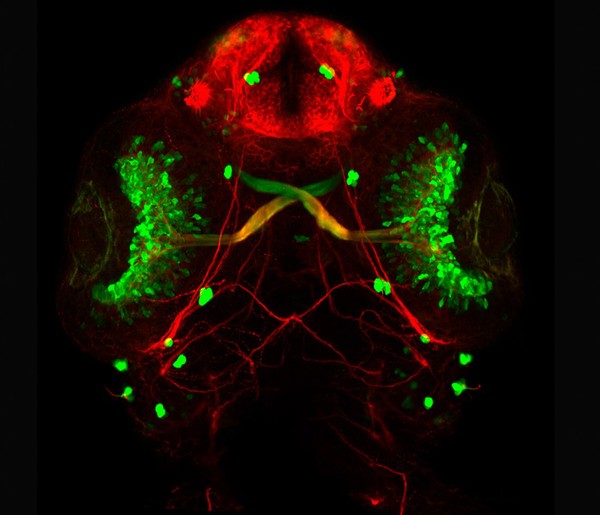
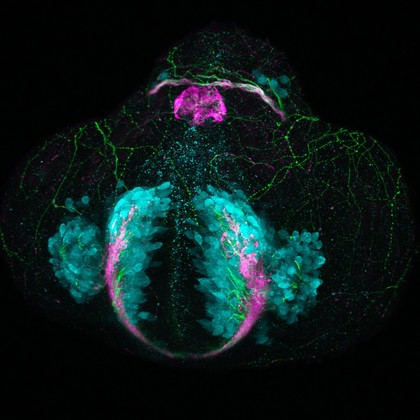
Zebrafish sensory neuromasts
Kate Turner, Dr Steve Wilson
- Digital Images
- Online
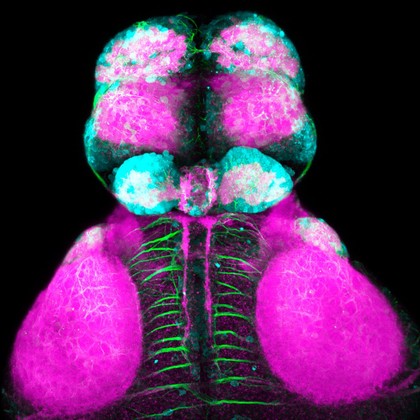
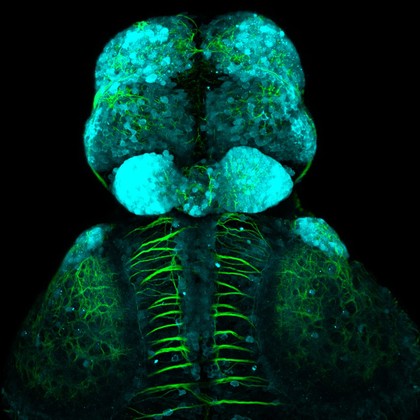
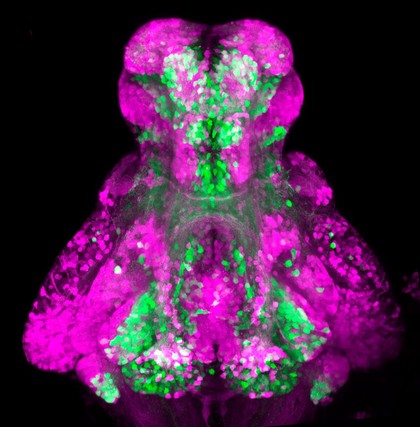
GABAergic and Glutamatergic neurons in the zebrafish brain
Kate Turner, Dr Steve Wilson
- Digital Images
- Online
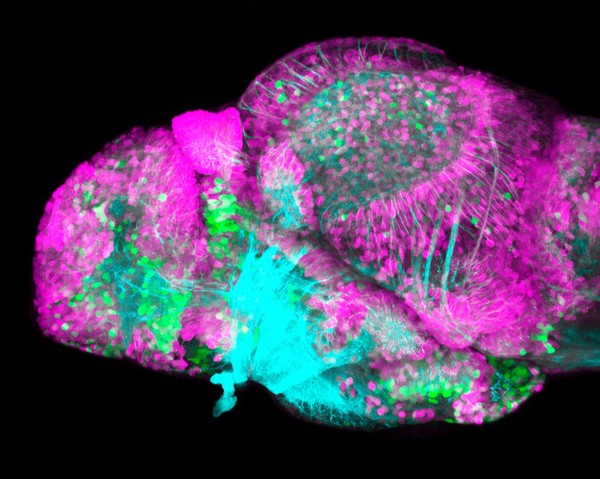
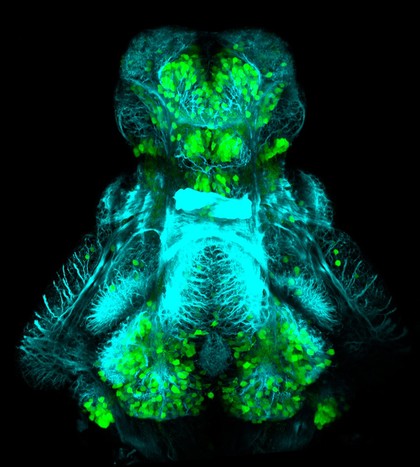
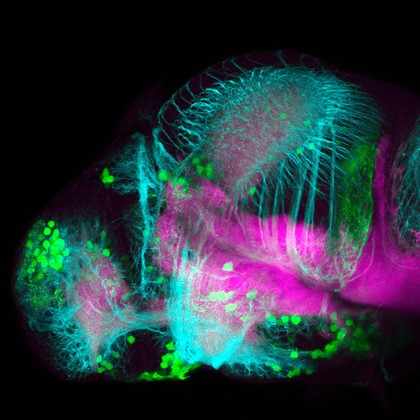
Dopaminergic neurons in the zebrafish forebrain. Confocal micrograph of a 4 day old transgenic zebrafish embryo viewed from a lateral aspect. Neurons in the olfactory bulb, telencepahlon, ventral diencephalon, pretectum and hypothalamus are labelled in green. Axonal tracts are shown in cyan and neuropil in magenta. In order to show the anatomy of the brain better the skin and eyes of the embryo have been removed post-fixation.
Kate Turner, Dr Steve Wilson
- Digital Images
- Online
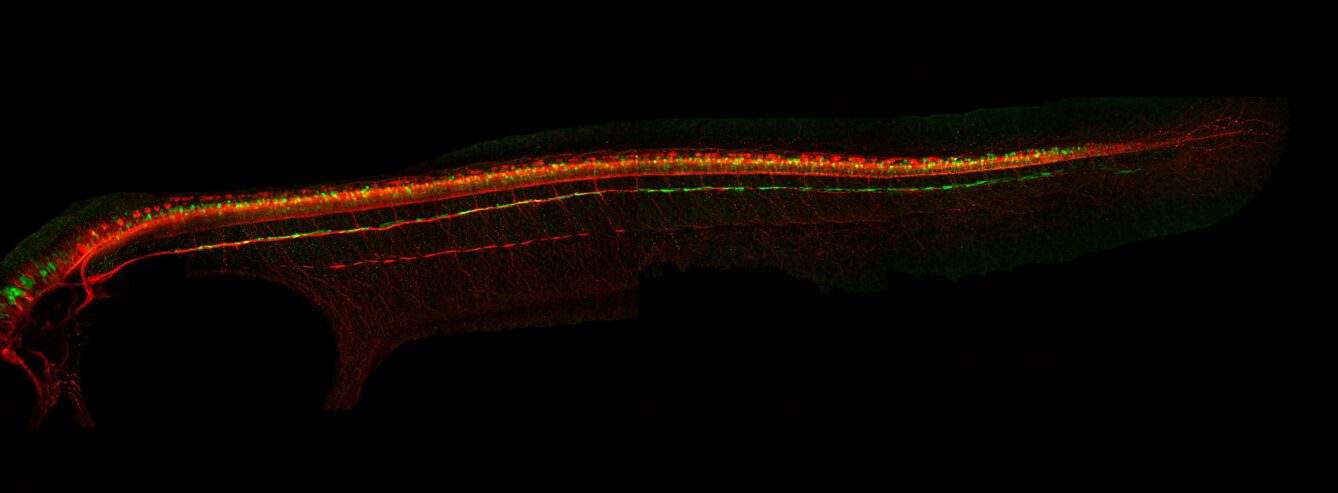
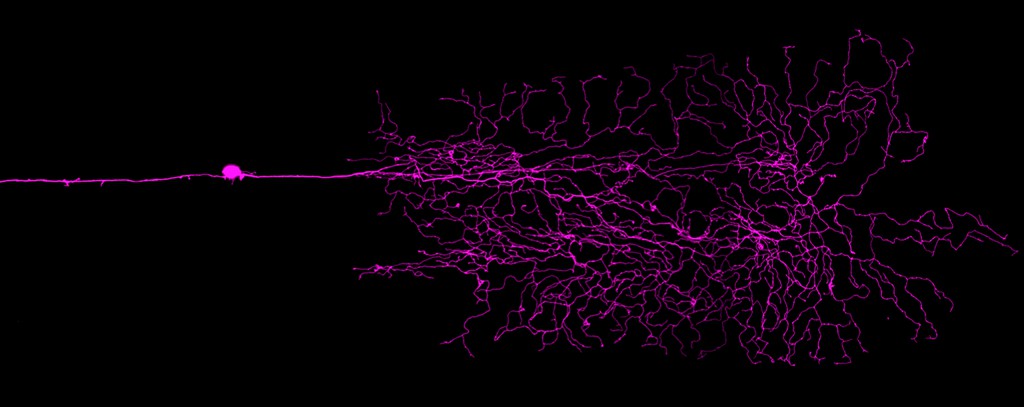
Glycinergic neurons in a zebrafish embryo
Kate Turner, Dr Steve Wilson